High Yield T7 RNA Poymerase
Description
T7 RNA Polymerase is Isolated from E.coli carrying a plasmid which contains the T7 RNA Polymerase gene. T7 RNA Polymerase is a DNA-dependent RNA polymerase that is highly specific for the T7 phage promoters.
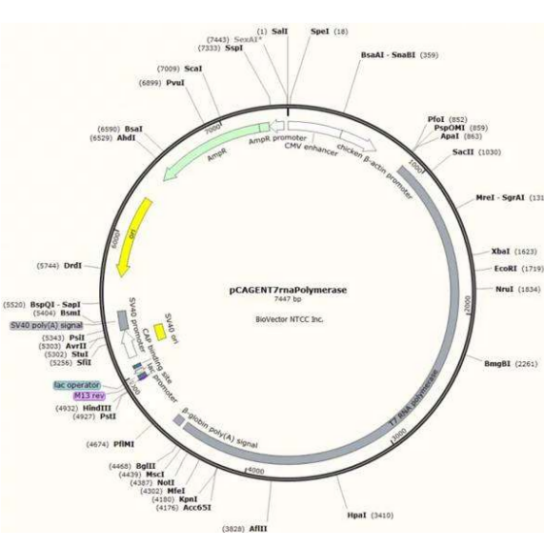
Chemical Structure
Unit Definition
One unit is defined as the amount of enzyme that will incorporate 1 nmol ATP into acid-insoluble material in a total reaction volume of 50 μl in 1 hour at 37°C in 1X RNA Polymerase Reaction Buffer.
Specification
| Test Items | Specifications |
| Protein Purity | ≥95% |
| Nickase | None detected |
| Rnase | None detected |
| Endonuclease | None detected |
| Exonuclease | None detected |
| Promoter Specificity | Nonspecific product≤1.5% |
| E.coli gDNA | ≤0.1 pg/50U |
| Endotoxin | LAL-Test, ≤10EU/mg |
Transportation and storage
Transportation: Dry ice
Storage: All components should be stored at -25~-15°C
Recommended re-test Life: 2 year
related products
Write your message here and send it to us